The importance of tires in a bike is often easily ignored. Tire characteristics are closely related to the performance and efficiency of the bike. Here to introduce the structure of the tire and the characteristics of the tire.
First of all, understanding the structure of the tire could help us find the right tire.
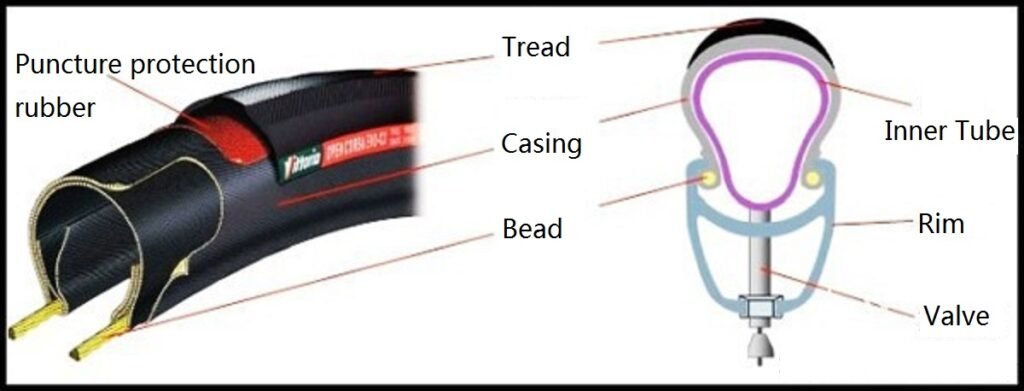
Tire construction
This is how the tires are constructed. An open tire (clincher) of a bicycle is the main body of a tire made up of a mesh cover, affixed with a layer of tire skin to grind the rolling time, and embedded in two tread lips to fix the tire to the wheel frame, thus forming the main structure of the tire. Because the bicycle tire is thin and easy to be punctured or cut, most of them add an explosion-proof layer between the tire skin and the mesh cover to increase the strength of the tire.
Characteristics of tires
Generally in describing the characteristics of the tire, is roughly divided into several directions: rolling resistance, grip, road sense, wear resistance, explosion-proof, weight, price. Besides, two features are often ignored but important: power transmission and manufacturing quality.
When the wheel starts rolling, you want it to keep rolling and not slow, which is impossible because it faces wind resistance and other resistance. In terms of the resistance of the bicycle itself, part of the reason is the resistance of the hub, and the other main part is the rolling resistance of the tire. The smaller the rolling resistance, the easier the speed is to maintain, in other words, you use the same strength to step faster.
TPI Woven Density
Because the web cover is the main body of the tire, and the main source of rolling resistance is the energy loss caused by the compression deformation of the web cover when it comes into contact with the road surface, the good quality of the web cover is the key to the tire performance. And the most common indicator is the density of TPI, webbing. Higher TPI means more fiber in an inch. High-density webs represent finer fibers and less rubber to fill gaps; relatively low-density webs have thicker fibers and more rubber to use.
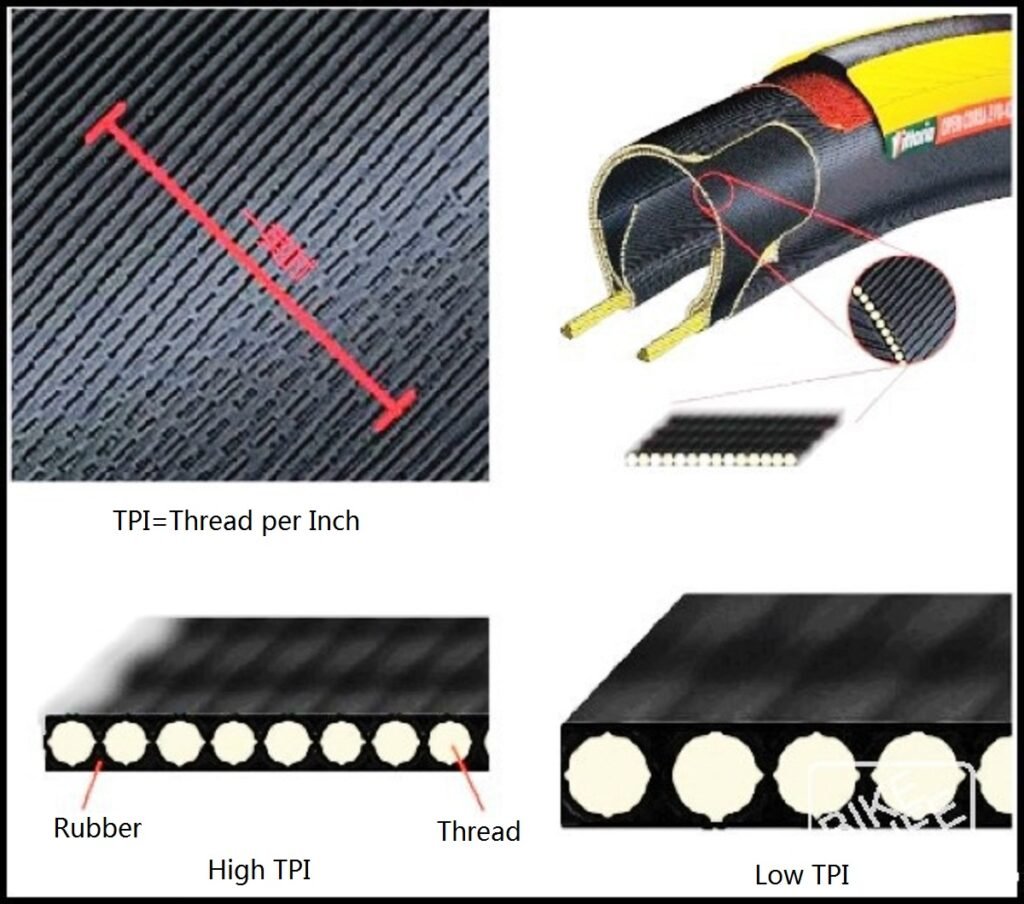
The influence of the mesh cover is very extensive. First of all, it is the main reason for the formation of tire road sense characteristics. The higher the mesh density, the thinner the mesh cover and the more sensitive the reaction. The maximum contact area with the ground can still be maintained when the uneven road is pressed, and the vibration will not spread. Low mesh density and heavy tread, when passing through rough roads, often too late to react, will vibrate directly to the palm or buttocks, and will let the tire jump off the ground, making the contact area smaller, the grip also become worse.

From the road sense can also derive high TPI other benefits: lightweight, low rolling resistance, better grip on the rough road surface, and better-associated power transmission. Because high TPI has so many benefits, why not achieve the highest mesh density per tire as much as possible? Partly because of industrial design and cost considerations, partly because of the division of the manufacturer’s product line, and partly because of the strength problem. The high TPI mesh cover must be thinner than the low TPI, and the explosion-proof characteristic is also poor. A short commute, a bike with a shock absorber, or simply a deliberate attempt to ride a bad road, do not require high TPI tires.

The particle tire is designed to increase grip on the soft ground
A wider tire, such as 1.5 inches or more, is designed to check for wear rather than drainage. At the speed of the bicycle and the floor area of the tire, it is not enough in the wetland to form a “water film” that will make the bike slip “. If it is a convex particle, it is to increase the grip on the soft pavement or the gravel pavement, because the pavement is softer than the tire, and the particles can sink in and bite the road, greatly increasing the grip. You can see what this means by looking at the tread prints that the beach bike has pressed on the beach. The road sense used on the hard ground by the particle tire must not be good, the grip is insufficient because of the reduction of the contact area, and the power transmission must be poor because part of the stepping force will be consumed in the deformation of the particle. Make the whole bike difficult to drag.

So thin road tire, what is the intention of designing tire lines? Not to drain, but to increase grip. The design of the tread is controversial because the common sense of the average person will think that there is a tread grip will be good, manufacturers to cater to the market so the introduction of the product with tread, but in fact, the connection between grip and tread is not conclusive. Some manufacturers claim that their treads can spread pressure and increase contact with the ground, and grip performance will increase. It is also said that fine tread can “penetrate” into the cracks in the road to increase grip.
The design of the tread increases the rolling resistance because it also consumes energy to compress and deform the tread. Fetal lines can also make the transmission of power worse because part of the force applied to the skin is consumed by the deformation of the tread. Tires with treads tend to have better characteristics, lower rolling resistance and better force conduction after flat treads. Although the manufacturer will explain the intention of designing the tire pattern, it does not mean that the skinhead tire will have insufficient grip under the same road condition, even the rolling resistance of the skinhead tire is lower. But apparently, tire treads seem more reassuring, as manufacturers design their products better.


